Measuring force in mechanical constructions became important in the early days of industrialization. Around 1940, a Strain gauge load cell was invented. A load cell is a transducer (sensor) that measures force, and outputs this force as an electrical signal. Most load cells use a strain gauge to turn material deformation/force in to an electric signal.
During the 1950s, load cells were implemented in tensile & compression testing machines. The load cell would most ideally be mounted just before or as close as possible to the contact point with the workpiece. The electronic system is designed to use the feedback to adjust the force application mechanism (motor) to apply only the desired force. Closed-loop systems work so well that today all electronic tensile/compression instruments exclusively use closed-loop control.A closed-loop system can constantly measure the test force being applied, and also the components used in a closed-loop system inherently lend themselves to a much simpler design than a dead-weight system. As mentioned on the DEAD WEIGHT systems page of this website, dead-weight systems require levers, pivots and other friction-inducing components to function efficiently.
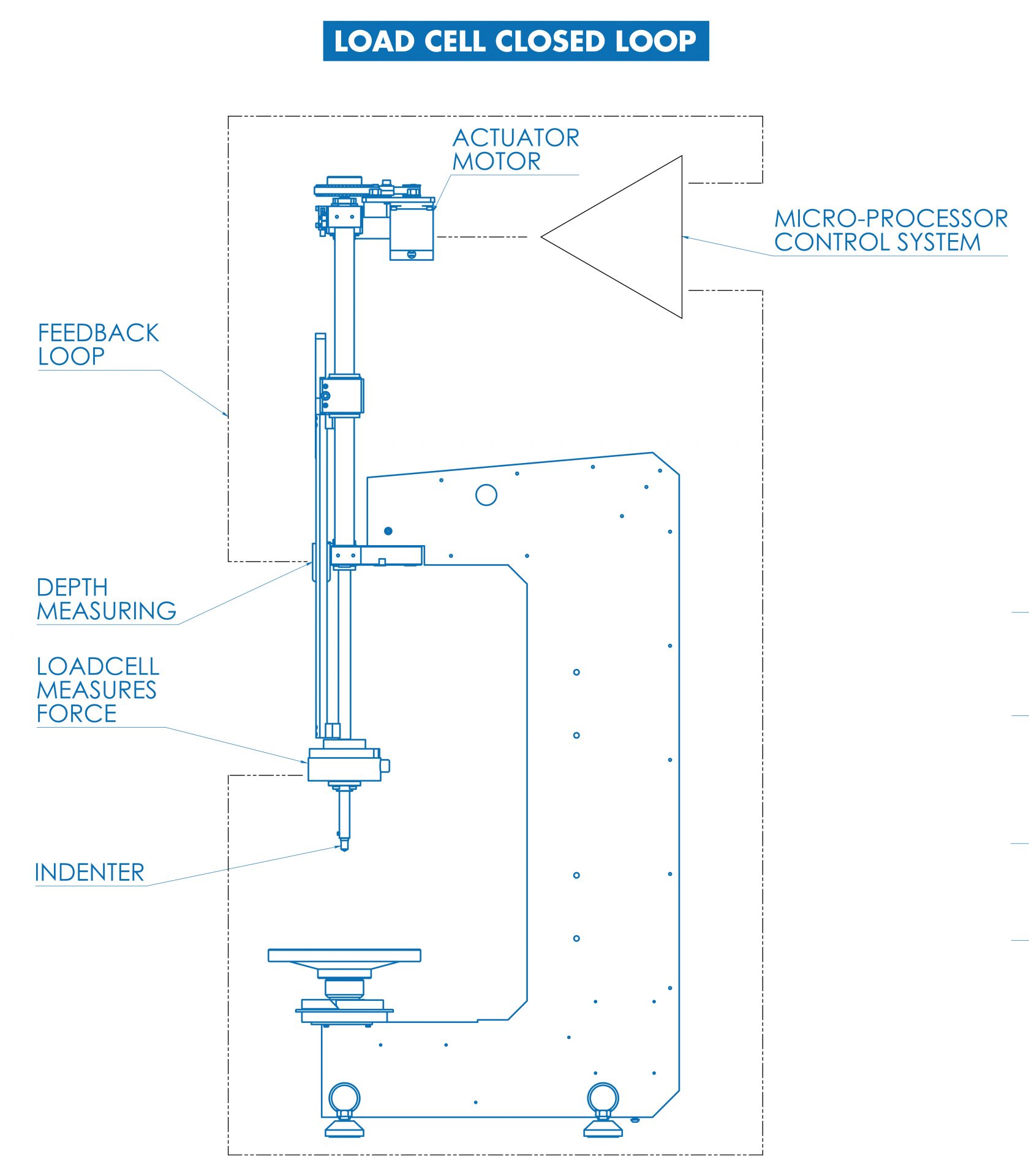
In a hardness tester, the indenter, the only part of the force system in contact with the test sample, is the most important element for a correct hardness measurement. To eliminate the effect of mechanical imperfection, mechanical moving or other disturbance that could affect the test force, the load cell should be installed as close as possible to the indenter.
Only in this way the real advantage of load cell based, closed loop systems come to their maximum force accuracy. Load cells placed on other positions in the hardness testers mechanical force actuator, rapidly lose most of their advantage over traditional dead weight systems.
INNOVATEST engineers have designed unique non-commercial load cells and force application systems that are the heart of each machine. Nearly all INNOVATEST hardness testers measure force at the indenter mount location to assure the maximum benefits of closed loop technology.
Advantages of closed loop system:
High accurate test forces
Force feedback assures correct force is applied
Wide range of test forces not depending on mechanical limitations
Faster test procedures
Reduction of mechanical parts comparing to dead weight systems
Simple electronic calibration procedure
Disadvantages of a closed loop system:
More expensive than a dead weight system
Requires electricity